There is a wide variation between the South Australian collecting organisations in their practices and stages of digitisation. In all cases, though, it is useful to consider the digitisation process as a cyclical workflow with ongoing digitisation, infrastructure, access and preservation requirements.
A Digitisation of South Australian Cultural Heritage Collections Feasibility Study, commissioned in 2020 by the South Australian Government, sets out the lifecycle framework for collecting organisations, based on international best practice. The key stages of the Digitisation Lifecycle Framework are summarised below.
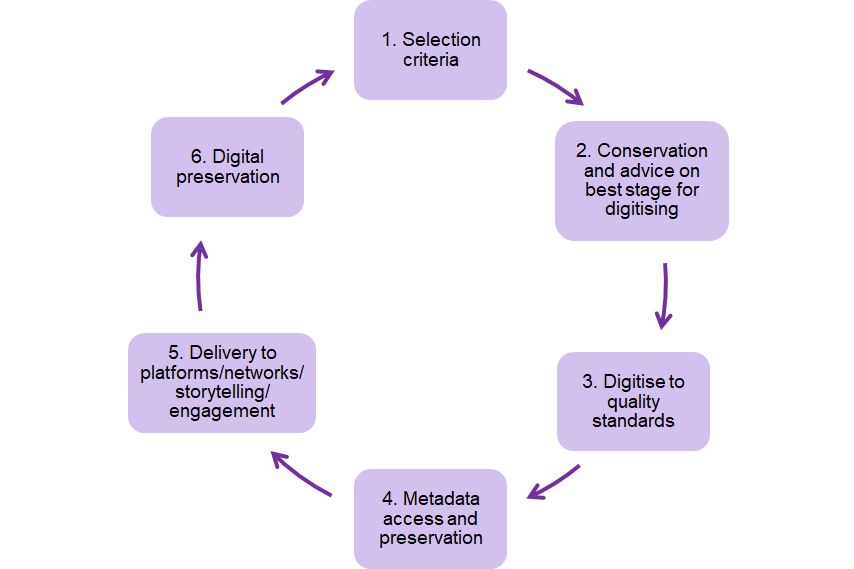
- Select Criteria
- Conserve/stabilise originals – advise on best stage for digitising
- Digitise to quality standards
- Metadata access & preservation
- Deliver to platforms/networks/storytelling/engagement
- Digital preservation
Rinse and repeat!
Table 1. Digitisation Lifecycle Framework Summary
| Stage | Description |
| 1. Select | Involves selecting objects or sub-groups for digitising, which requires prioritising according to selection criteria (Framework) and creating digitisation plans. |
| 2. Stabilise/ Conserve | Involves: – stabilising or conserving original objects so that they can be digitised without causing damage – careful handling of fragile originals and providing handling advice to digitising staff – determining the best stage for digitisation to take place – re-housing of objects afterwards, as required. |
| 3. Digitise | Digitisation to quality and technical standards. |
| 4. Metadata | Standardised descriptions about what the content is, where it came from and who can use it. Metadata enables digitised objects to be stored, found and used into the future. |
| 5. Delivery/Engagement | Involves: making the content accessible to users via a range of delivery platforms and networks, curating the digitised objects to tell their stories providing innovative ways for users to access and engage with digital content. |
| 6. Digital Preservation | Sustainable storage and management of digitised items into the future, including planning for technology changes, backups and long-term storage plans. For funded (non-volunteer) organisations a digital preservation system should be considered. |
More on selecting items for digitisation in the Selection Framework.
